blog posts
magma In
ALL BLOGS
To build opensource community around 5G ecosystem
My Posts
All5G5G Call Flow5G Core5G RAN PROTOCOLRAN ProcedureUncategorized
NR Frame Structure
By heliumJuly 10, 2022UncategorizedBy Shubham Kumar Data(UL/DL) is transmitted in the form of radio frames in the air. Radio Frames are of a duration of 10ms which consists of 10 subframes each having a duration of 1ms. Subframes inside a radio frame are serialized as SF0, SF1, SF2, SF3, …., and SF9. This arrangement of frames and subframes is …
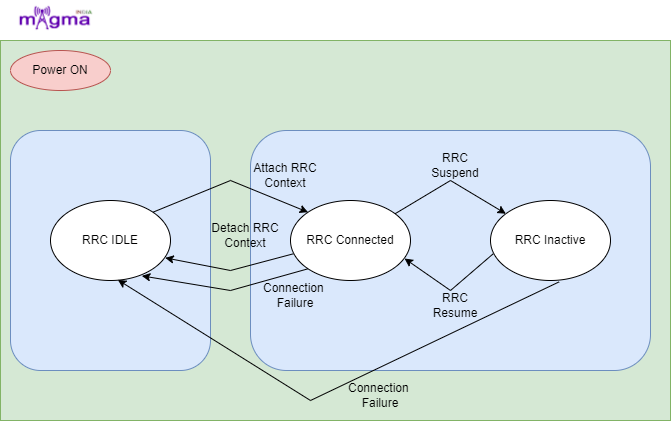
5G UE STATE MANAGEMENT
5G UE STATE MANAGEMENT
By Nitin RajputJune 16, 20225GIn 5G, it provides different services to the devices. For providing that service is the 5G system, it needs to track the availability and also the reachability of the device. 5G system tracks these states of the device such as:- RRC (radio resource control), Connection Management (CM), and Registration management (RM). RRC determines the RRC …

SSB AND PBCH
SSB AND PBCH
By Nitin RajputJune 7, 20225GPBCH It carries the broadcast information known to be as MIS (minimum system information). It carries information like SSB index, half-frame number and system frame number. It is also used for frame and slot synchronization. Now, the modulation used for PBCH is QPSK modulation and it also has the DMRS signals used to know the …

SERVICE BASED ARCHITECTURE
SERVICE BASED ARCHITECTURE
By Nitin RajputJune 4, 20225GMicroservices When the large applications are broken down into the different small services it’s known to be microservices. Each service is performing the desired task and they can communicate with each other through an interface which is known as the SBI (service-based interface). By using the microservices architecture, they provide flexibility like different services performing …

MAC SCHEDULER ( UPLINK AND DOWNLINK SCHEDULING )
MAC SCHEDULER ( UPLINK AND DOWNLINK SCHEDULING )
By Nitin RajputMay 30, 20225G RAN PROTOCOLThere is a finite set of time and frequency resources. These resources are dynamically allocated to the different connected devices (UE) that are accessing the 5G network, in such a manner that they will efficiently serve the network. This is known as shared channel transmission. The main function of scheduling is to decide which devices …
MAC SCHEDULER ( UPLINK AND DOWNLINK SCHEDULING ) Read More »

RAN PROCEDURE PART-2: RANDOM ACCESS
RAN PROCEDURE PART-2: RANDOM ACCESS
By Nitin RajputMay 26, 2022RAN ProcedureThrough initial access, the device was able to find out the cell. Now with the random access procedure, the device will be able to access the cell. It was triggered in some different scenarios such as i) whenever the UE goes from RRC idle to RRC connected mode (maybe due to the device getting switched …

RAN PROCEDURE PART-1: INITIAL ACCESS
RAN PROCEDURE PART-1: INITIAL ACCESS
By Nitin RajputMay 25, 2022RAN ProcedureThere was a 5G mobile and it was turned on. The first procedure to happen is cell search and cell selection when the phone is turned on. This allows the phone to find a cell. Cell search is the procedure by which the UE requires the time and frequency synchronization with the cell and detects …

NETWORK SLICING
NETWORK SLICING
By Nitin RajputMay 24, 20225GNetwork slicing overlays multiple virtual networks on top of a shared network. There are some limits imposed by the physical networks. The idea of living is to use an underlying physical network and takes its capabilities and divide it into the logical section where each section can have different performance characteristics. Now for different performance …

5G CALL FLOW PART-4: SERVICE REQUEST PROCEDURE
5G CALL FLOW PART-4: SERVICE REQUEST PROCEDURE
By Nitin RajputMay 23, 20225G Call FlowThis is the procedure which is used when the device wants to establish a connection to the AMF. There are two possible scenarios in which this can happen i) this can be used when the device does not have a connection to the AMF and hence uses this procedure to establish a new connection. In …

5G CALL FLOW PART-3: PDU SESSION ESTABLISHMENT PROCEDURE
5G CALL FLOW PART-3: PDU SESSION ESTABLISHMENT PROCEDURE
By Nitin RajputMay 22, 20225G Call FlowWhenever a new PDU Session is created, then this procedure is employed. Alternatively, when a PDU Session is handed over from non-3GPP access like Wi-Fi, at that time the PDU Session establishment procedure is used. Typically this procedure is always initiated by the device. But if the network would like to trigger it, then it …
5G CALL FLOW PART-3: PDU SESSION ESTABLISHMENT PROCEDURE Read More »

5G CALL FLOWS PART-2: DEREGISTRATION PROCEDURE
5G CALL FLOWS PART-2: DEREGISTRATION PROCEDURE
By Nitin RajputMay 21, 20225G Call FlowWhen a device wants to access the services of the 5G system. It has to register itself with the network. When it is no longer wants to access the services, it has to deregistered from the 5G network. This is known as the deregistration procedure. The network can also initiate the deregistration procedure when it …

5G CALL FLOWS PART-1: REGISTRATION PROCEDURE
5G CALL FLOWS PART-1: REGISTRATION PROCEDURE
By Nitin RajputMay 20, 20225G Call FlowWhen a 5G device is first turned ON, it needs to register itself with the network before accessing the 5G services. This process is known as registration. But power on is not only the situation when this registration happens. It can be defined in four categories as i) Initial Procedureii) Periodic Procedureiii) Mobility Procedureiv) Emergency …

5G IDENTIFIER
5G IDENTIFIER
By Nitin RajputMay 19, 20225GIDENTIFIERS IN 5G Identifiers are used who uniquely recognize the entity. Send all the connection characteristics are tied to this identity. For example, if the device identity can be used it will be fine if it is a blacklisted device or not. Subscription identity is used to define if the subscription allows a certain 5G …

5g core network function part 5: PCF
5g core network function part 5: PCF
By Nitin RajputMay 16, 20225G CorePolicy Control Function The policy is simply a rule for how the 5G system can manage the different users, data sessions or different data flows. The policy themselves can be specified as different levels of granularity such asi) some policies affect all the users in the same mannerii) some policies are user-specific, but it affects …

5G CORE NETWORK FUNCTION PART-4: UPF
5G CORE NETWORK FUNCTION PART-4: UPF
By Nitin RajputMay 15, 20225G CoreUser Plane Function The primary role of UPF in a 5G system is to provide interconnections toward the external data network. Data networks can be the Internet, IMS, enterprise system etc. In any case, we need UPF to provide connectivity between the 5G network and the data network. 5G technology is itself a mobile technology …

5G CORE NETWORK FUNCTION PART-3: UDm, UDR
5G CORE NETWORK FUNCTION PART-3: UDm, UDR
By Nitin RajputMay 13, 20225G CoreStateless Design If an application and designed in a way that the application logic is handled by the application entirely and that data lies entirely outside of the application function. Then it is called a stateless design. So we need to keep data, entirely decouples from the application logic. Unified Data Repository It is the …

5G CORE NETWORK FUNCTION PART-2: SMF
5G CORE NETWORK FUNCTION PART-2: SMF
By Nitin RajputMay 12, 20225G CoreSession Management Function It is a control plane function in a 5G core network. SMF’s main function is PDU Session Management. PDU Session Management It is simply a logical connection between the device and the end of the user plane function (UPF) which in turn connects to the data network (DN) through the N6 interface. …

5g core network function part-1 : amf
5g core network function part-1 : amf
By Nitin RajputMay 11, 20225G CoreAccess and Mobility Management Function It is a control plane function in a 5G core network. AMF’s main function is as follows 1. Registration Management When the device is turned on, the device has to try to connect to the network, and then due-process it has to verify and validate that it is connecting to …

RAN PROTOCOL STACK PART-3: PHY (Functions), NAs, rrc
RAN PROTOCOL STACK PART-3: PHY (Functions), NAs, rrc
By Nitin RajputApril 30, 20225G RAN PROTOCOLRead the first part here: https://blog.magmaindia.org/ran-protocol-stack-sdap-pdcp-rlc/ Read the second part here: https://blog.magmaindia.org/ran-protocol-stack-mac-phy-part-2/ 5. PHY-Layer (functions) CRCFirst we need a mechanism to detect error on the level of transport block. For this purpose CRC(Cyclic Redundancy Check) is calculated and added to the transport block. On the receiver side, CRC can be used to detect error in …
RAN PROTOCOL STACK PART-3: PHY (Functions), NAs, rrc Read More »

Ran Protocol Stack Part-2: MAC , PHY
Ran Protocol Stack Part-2: MAC , PHY
By Nitin RajputApril 27, 20225G RAN PROTOCOLRead the first part here: https://blog.magmaindia.org/category/5g-ran-protocol/ 4. MAC (Medium Access Control) These are the functions of Mac :- 1. Logical-channel multiplexing 2. Hybrid-ARQ retransmission 3. Scheduling 4. Multiplexing/Demultiplexing for carrier aggregation Multiplexing Logical Channel MAC layer provides the services to the RLC in the form of logical channels. MAC layer uses services from PHY layer …

Ran Protocol Stack ( SDAP, PDCP, RLC) Part-1
Ran Protocol Stack ( SDAP, PDCP, RLC) Part-1
By Nitin RajputApril 25, 20225G RAN PROTOCOLThere are two different types of Ran Protocol Stack as follow 1) User-Plane Protocol Stack 2) Control-Plane Protocol Stack Lets us discuss with the help of diagram USER-PLANE PROTOCOL STACK It supports in carrying the user data network between different applications of user equipment and in the network. Each layers shown in above diagram provides …
